Breaking Down the Real Meaning of an XDR Solution
Read More Stay ahead of evolving cyber threats with effective defense strategies. Learn how
Want to stay ahead of threats in 2025? This research report is all you need to stay updated.
Cloud computing is changing how companies handle their data, providing unparalleled scalability and flexibility. Gartner predicts that by 2025, 85% of businesses will primarily use cloud services. But this change also brings in associated security risks. The 2023 Cloud Security Report by Cybersecurity Insiders found that 93% of companies are concerned about security risks in the cloud.
As more businesses move to the cloud, making sure they have good security measures is very important. Failing to have solid security can cause data leaks, compliance violations, and costly downtime. In this piece, we’ll talk about what to look for in cloud security and how to protect your cloud infrastructure.
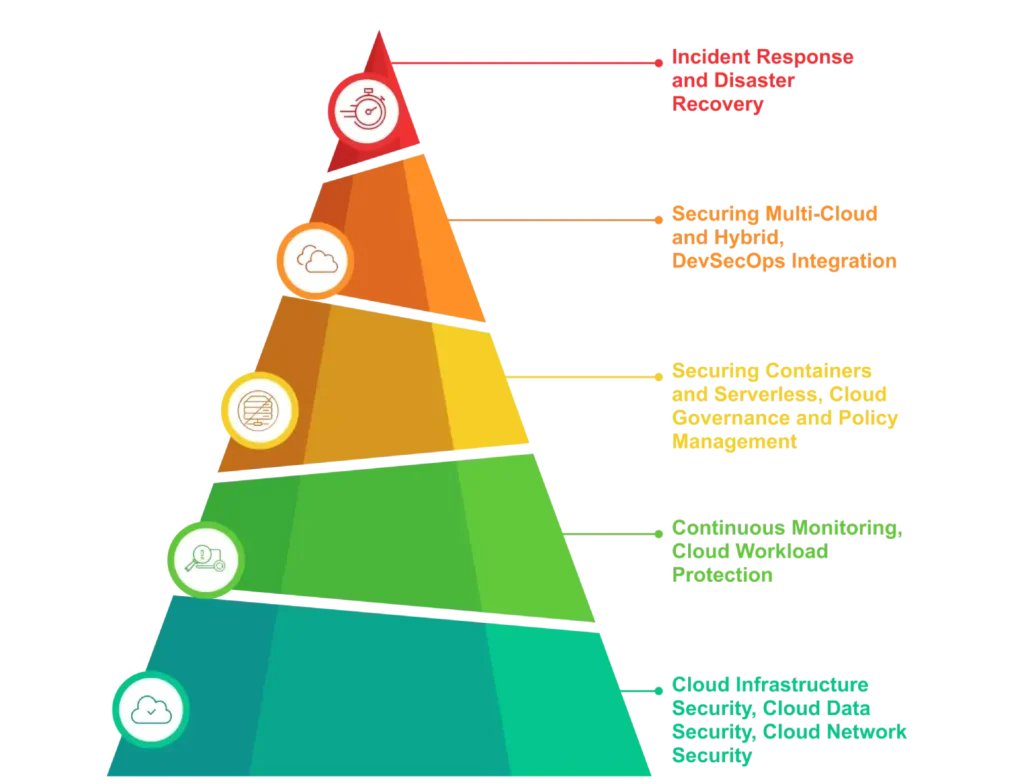
Cloud infrastructure security serves as the bedrock of any cloud ecosystem, thereby protecting Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS) from attacks. To attain this, three components, in particular, play an important role: Identity Management and Access Control (IAM), encryption, and automated compliance monitoring.
IAM is a system that controls who can access what within your cloud ecosystem. This system ensures control so that only authorized users have access to crucial cloud resources.
Here’s how IAM enhances security:
IAM helps to mitigate internal threats and prevent unauthorized access, by allowing users to have only those resources which are necessary for their job.
Encryption secures your information by encoding it so that it cannot be read by any unauthorized party, whether at rest or in transit.
Here’s why both types of encryptions are crucial:
Tools for compliance that are automatic help to understand how safe the cloud infrastructure is. For example, GDPR or HIPAA would be such industry standards and would not only be met, but violations of them would also be consistently checked for.
| Key Security Measures | Description |
|---|---|
| IAM | Controls access to resources, ensuring that only authorized users can access data. |
| Encryption | Protects data from unauthorized access by encoding it both at rest and in transit. |
| Compliance Automation | Continuously monitors compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. |
Safeguarding data is crucial for cloud security. Data leaks can cause serious damage, affecting both the finances and reputation of an organization. Effective cloud data security includes tools such as Data Loss Prevention (DLP), multi-layer encryption, and Cloud Data Security Posture Management (DSPM).
DLP monitors and controls how sensitive data moves within cloud systems, preventing unauthorized sharing or loss. In an example, if an employee tries to transmit confidential client information through an unsecure email service or external cloud services, DLP systems will stop the action and notify the security team.
In this comprehensive buyer’s guide, you’ll discover:
Multi-layer encryption is another important aspect of cloud data security. This sort of security ensures that the information and data are encrypted not only when it’s stored on cloud servers but also when it’s being transmitted over the different networks. This two-step approach provides extra security, especially for very sensitive data like personal information, financial details, or intellectual property.
Cloud Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) provides organizations with the ability to track the security status of their stored data in the cloud. It is used by security teams to determine the storage locations of sensitive data, who can access it, and if it’s at risk because of misconfigurations or unauthorized access attempts.
By combining DLP, encryption, and DSPM, organizations can make sure that the cloud data is safe and compliant, and that there are measures to protect it against both internal and external threats.
| Data Security Solutions | Purpose |
|---|---|
| DLP | Prevents unauthorized data transfers, securing sensitive information. |
| Multi-Layer Encryption | Protects data at multiple levels to strengthen overall security. |
| DSPM | Monitors data security risks in real time, reducing exposure to breaches. |
Cloud network security aims at securing data exchange through cloud resources and maintaining secure communication channels within the cloud. One of the components of cloud security is the Zero Trust Architecture, which states that no user, device or system is trusted by default. Rather than allowing access by default, the Zero Trust policy requires that all access points be authenticated and verified. For example, even if a device is connected to the company’s network, it must first authenticate itself and demonstrate its legitimacy before it can access any cloud resources, thus limiting the chances of unauthorized access by malicious users.
Micro-segmentation is another important aspect of cloud network security as it effectively breaks down the cloud network into separate segments. This segmentation decreases the threat of lateral spread in the event that one segment is compromised. For example, it is possible for an attacker to infiltrate a specific cloud workload, but micro-segmentation will restrict them from moving between workloads or systems. Such a containment strategy lowers the impact inflicted by a breach and the associated costs.
Furthermore, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are crucial for monitoring network traffic for any unusual activity, like unauthorized data access. These systems catch threats as they happen and can automatically stop harmful actions, keeping the cloud network safe and strong against attacks.
| Network Security Techniques | Description |
|---|---|
| Zero Trust Architecture | Continually verifies access requests, minimizing risks of credential compromise. |
| Network Micro-Segmentation | Divides the network to prevent threats from spreading across cloud services. |
| IDS/IPS | Monitors and prevents malicious activity within the cloud network. |
Considering cloud environments are dynamic in nature, constant monitoring and threat detection become crucial for the security component. It is necessary that all cloud systems are capable of real time detection and response to reduce damage and stop breaches.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools are often used within the cloud to gather and analyze security events across the cloud for the purpose of managing incidents. SIEM systems offer insight into all the things happening within a system including users’ activity, access habits, and system updates, which help the security team to catch unusual behavior before it turns into a serious breach.
Another important aspect is behavioral analytics, which means looking at how users and systems act to find any unusual changes from what is normal. For example, if a user starts downloading a lot of important data at a strange time, behavioral analytics will notice this and raise concern, leading to an investigation. This kind of monitoring is useful for identifying insider threats or subtle hacking attempts that might go unnoticed by traditional security tools.
Also, clear and accurate alerts are important so that security teams don’t get overwhelmed by false positives. These alerts help teams focus on the serious issues, allowing them to deal with the biggest risks to the company. By using constant monitoring, behavioral analytics, and good alert systems, companies can stay ahead of attackers and respond fast to security problems.
| Monitoring Tools | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| SIEM Integration | Centralizes security event management, improving threat detection capabilities. |
| Behavioral Analytics | Identifies unusual activities, signaling potential insider threats or malware. |
| High-Fidelity Alerts | Prioritizes alerts based on severity to improve response efficiency. |
The focus of Cloud Workload Protection is on keeping the applications and processes running in cloud environments safe from unauthorized access and attacks. Workload isolation, which keeps different workloads apart, lowering the risk of one affecting the others.
Suppose that an application serving the purpose of financial transactions gets hacked into. Workload isolation stops the attacker from moving to other workloads, like those managing customer data or internal communication systems. This containment method reduces the harm a breach could cause.
A key part of protecting workloads is managing their security settings properly. This is done by using automated systems to enforce security policies consistently across all workloads. Cloud environments change frequently, with workloads being set up, scaled, and adjusted often. Managing these settings manually can lead to errors, which can cause security vulnerabilities. By using automated systems, organizations make sure that workloads always have the right security configurations, lowering the chance of misconfigurations. These automated tools can also check for and fix any security issues that come up, keeping all workloads secure at all times.
| Workload Protection | Description |
|---|---|
| Workload Isolation | Ensures workloads remain isolated, preventing cross-environmental threats. |
| Configuration Management | Enforces security policies and reduces misconfigurations through automation. |
With organizations using containers and serverless setups more for their cloud services, keeping these environments safe has become very important. Even though containers enable more efficient ways to run applications, they present new security risks as well. Therefore, it’s crucial to protect containers while they’re running, making sure malicious code can’t modify or compromise them.
This protection entails monitoring containers for suspicious actions, like unauthorized file modification or unusual network activity, and shutting them down if a security threat is detected.
Serverless computing eliminates the need to handle infrastructure, but it presents its own security issues. Since serverless functions are temporary and constantly changing, it’s important to have visibility into these ephemeral workloads to find any possible vulnerabilities or misuse. Security solutions like Fidelis Halo® offer real-time monitoring and protection for both containers and serverless setups, making sure these flexible technologies can be used safely. By focusing on the unique specific needs of containers and serverless functions, companies can enjoy the benefits of these modern systems without risking their security.
In this datasheet, you’ll learn:
| Container and Serverless Security | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Runtime Protection | Protects containerized applications during execution. |
| Visibility for Serverless Workloads | Monitors serverless functions to detect vulnerabilities. |
| Fidelis Halo® | A unified platform offering real-time security for containers and serverless computing. |
Cloud governance means making sure that security policies are always followed and enforced in the cloud, regardless of how dynamic or distributed it may be. When the cloud setup changes—like when it scales, adds new services, or moves tasks around—security policies need to change too, to keep everything safe. Using automated policy creation tools are important to keep security policies updated, as they dynamically generate policies that fit the current cloud setup. This helps prevent security risks that happen when policies are outdated.
Efficient management of policies also necessitates a certain degree of control over all the cloud resources as well as the security configurations. Unified governance platforms provide solutions for security personnel to manage the implementation of the policies across several clouds (like hybrid or a multi-cloud) from single console. Compliance and security controls will therefore be implemented across all cloud resources, thus reducing the risk of misconfigurations or policy violations.
By automating policy setup and centralizing control, companies can keep strong security measures in place, even in complex multi-cloud environments.
| Cloud Governance Solutions | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Automated Policy Management | Ensures security policies remain consistent as cloud infrastructure evolves. |
| Unified Governance Platforms | Streamlines policy enforcement and ensures regulatory compliance. |
As companies start using multi-cloud and hybrid environments, keeping everything secure gets harder. Multi-cloud environments use services from various providers like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. And hybrid setups combine on-premises infrastructure with cloud platforms. To protect these different setups, a single, consistent security plan is needed to cover all platforms.
The first thing to focus on is getting cross-cloud visibility. When workloads and data are spread across clouds, it’s easy for security gaps to form, especially if each cloud is managed separately. Being able to track things in all cloud environments helps security teams find vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, or unauthorized access attempts, no matter which cloud it’s on.
Using security tools that work with multiple cloud providers is important for monitoring these environments and managing them well. Such tools help in identifying risks and make sure security policies are followed across all cloud services.
Moreover, having multi-tiered security is very important for protecting different layers of cloud infrastructure. In a setup that uses multiple clouds or a hybrid environment, it’s essential to use special security measures for each layer, like the network, data, and application layer.
For example, encrypting data can help protect important information in the data layer, while using Zero Trust access controls at the network layer can control who can use cloud resources. By using a layered security approach, companies can handle the different risks in each layer of the cloud, making sure that security is strong and fits the needs of each environment.
| Multi-Cloud Security | Features |
|---|---|
| Cross-Cloud Visibility | Provides visibility into security risks across multiple cloud platforms. |
| Multi-Tiered Security Model | Targets security at various levels within cloud infrastructure for enhanced protection. |
DevSecOps is a practice of combining security with the DevOps pipeline, making sure that security is included at every stage of software development. In the past, security was usually handled separately, often only after the development was finished. This approach resulted in security issues being found late, which could cause delays and leave systems vulnerable. DevSecOps changes this by making security everyone’s responsibility from the beginning, allowing for quicker development without compromising security.
The core benefit of DevSecOps is automated vulnerability scanning. As developers write their code, automated tools continuously look for any vulnerabilities, making sure they are found and fixed early on. This lowers the chance of insecure code being pushed to production and helps companies release it faster.
Also, the process includes checks to make sure the security measures are aligned with industry regulations from start to finish. This automation greatly reduces the work security teams have to do manually and ensures that all software releases meet the necessary compliance requirements from the beginning.
| DevSecOps Practices | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Automated Vulnerability Scanning | Identifies security flaws early in the development cycle. |
| Continuous Compliance Testing | Ensures compliance with industry standards throughout the development process. |
Regardless of how strong your cloud security measures are, incidents can still occur. This is why having a good plan for responding to incidents and recovering from disasters is crucial. It helps reduce the harm and downtime caused by breaches or system failures. Incident response involves quickly identifying, containing, and fixing security issues, while disaster recovery makes sure that important systems can be restored after an attack.
An essential component of incident response is automated response systems. These systems help companies act in real-time. While threats like unauthorized access, data exfiltration, or a DDoS attack are taking place, automated response tools can isolate the compromised resources. This quick action helps a lot in reducing the impact, data loss and system downtime caused by the incidents.
Disaster recovery plans aim to get things back to normal after a big problem, like a natural disaster, a cyberattack, or a hardware issue. Cloud-based disaster recovery (DR) is very helpful because it replicates important systems and data to the cloud, allowing for fast recovery even if the primary setup is damaged.
These cloud-based DR systems provide automatic backups and the ability to switch to backup systems quickly, so businesses ca backups are also important for disaster recovery, as they make sure the latest version of important data is available if a recovery is needed.
With a clear incident response and disaster recovery plan, companies can be ready for unexpected events, reducing both financial losses and damage to their reputation while keeping their business running smoothly.
| Incident Response and DR Solutions | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Automated Incident Response | Provides immediate remediation of detected threats, reducing impact. |
| Cloud-Based Disaster Recovery | Ensures quick restoration of data and services after an outage or attack. |
| Regular Backups | Maintains data integrity and reduces downtime following incidents. |
Understanding what to look for in cloud security is really important for businesses operating in cloud environments. By emphasizing strong identity controls, data encryption, constant monitoring, managing multiple cloud services, and having a proper incident response, businesses can protect their cloud infrastructure.
Incorporating security into the development process and maintaining clear governance ensure long-term safety and compliance. Tools like Fidelis Halo® provide comprehensive security solutions that improve visibility and protection across cloud platforms.
Sarika, a cybersecurity enthusiast, contributes insightful articles to Fidelis Security, guiding readers through the complexities of digital security with clarity and passion. Beyond her writing, she actively engages in the cybersecurity community, staying informed about emerging trends and technologies to empower individuals and organizations in safeguarding their digital assets.
See Fidelis in action. Learn how our fast and scalable platforms provide full visibility, deep insights, and rapid response to help security teams across the World protect, detect, respond, and neutralize advanced cyber adversaries.