Breaking Down the Real Meaning of an XDR Solution
Read More Understand how the malware Agent Tesla is silently stealing data from your
Exclusive Webinar: Your NDR is not doing enough! Find out what you need to supercharge it!
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack is an attempt to overload and disrupt the normal functioning of a server, service, or network by overwhelming it with traffic from multiple sources. In this type of attack, the attacker uses a group of devices infected with malware, commonly known as a "botnet" to bombard the target continuously with more requests than it can handle, which causes the server resources to run out and slow down or completely block legitimate users.
Now that we’ve explained what is a DDoS attack, let’s dive deeper into what is DDoSing and how these attacks operate as a deeper understanding of these attacks reveals their complexities and the strategies employed by attackers to launch large scale service disruption.
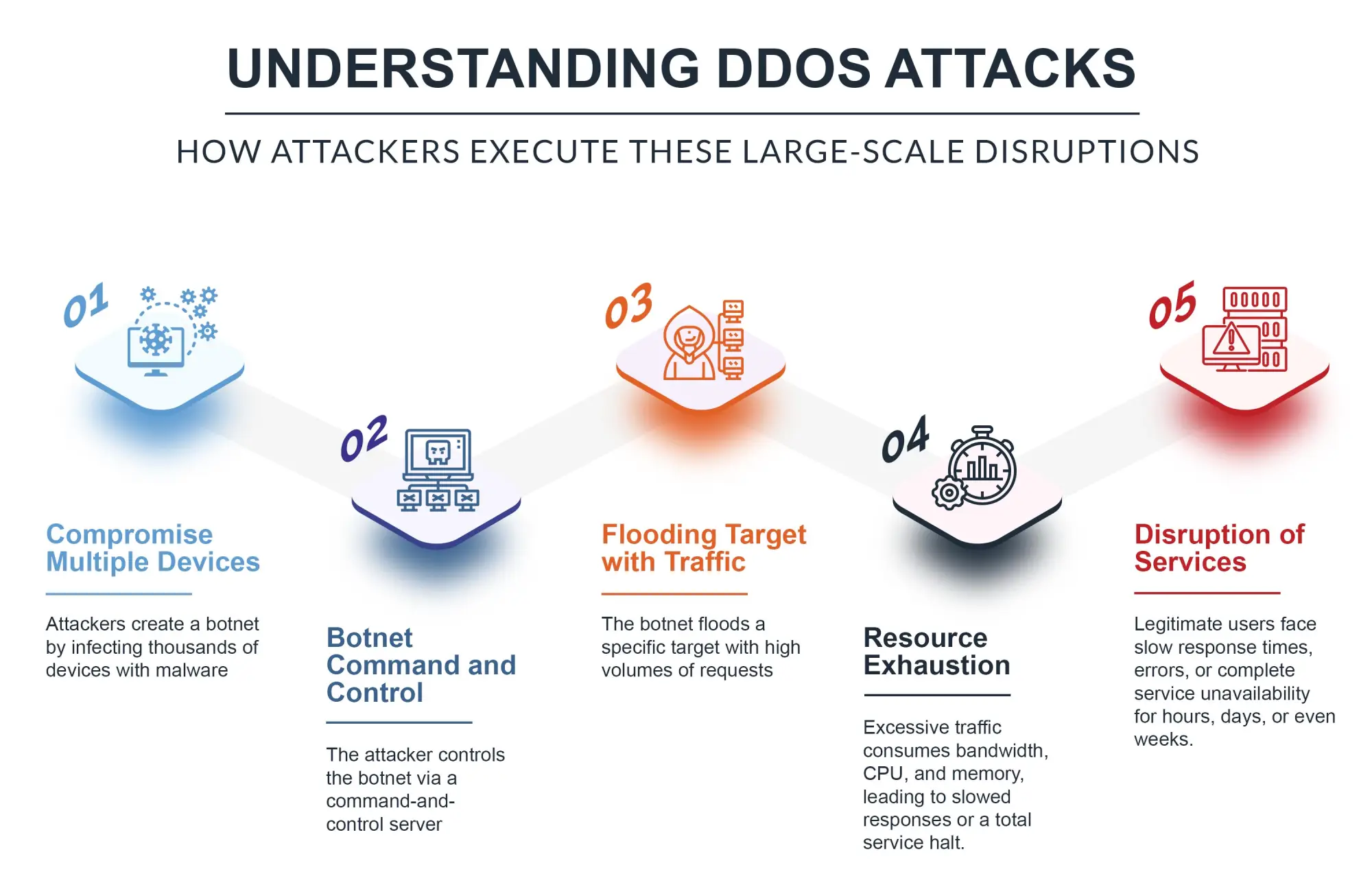
Compromise Multiple Devices: The initial phase of a DDoS attack involves assembling what is known as a botnet. Botnet DDoS is a group of compromised devices. In the majority of cases, attackers contaminate thousands of equipment and take control via malware or vulnerability in a vulnerable machine — with computers, IoT devices, routers, or even security cameras being the typical victims.
Botnet Command and Control: The botnet is under the attacker’s influence from a command-and-control (C&C) server. The attacker makes use of the C&C server to interact and convey instructions to launch an attack.
Flooding Target with Traffic: When the attacker is ready, they command the botnet DDoS to flood one server/network/application with as much traffic as possible. That traffic can be HTTP requests, UDP packets, or some other protocol depending on the kind of DDoS attack launched. The influx of traffic that gets directed at a target overwhelms its resource.
Resource Exhaustion: The quick increase of traffic to consume all the target bandwidth, CPU, and memory until it cannot provide real services anymore. Users will experience problems like slowed response times, errors or an outright denial of access.
Disruption of Services: Users are commonly unable to reach the affected service as long as the DDoS attack continues. It can run for hours, days, and in certain situations for weeks depending on the power of a botnet and determination of an attacker.
Distributed denial of service attack is broadly divided into three categories:
Volumetric DDoS attacks are done with the intention to overwhelm the server with the massive amount of traffic, saturate its bandwidth and prevent the server from responding to legitimate requests. The magnitude of attack is measured in bits per second. This includes flood attacks like UDP, ICMP, HTTP, CharGen. The whole attack is done by sending enough packets in the network which force the server to crash or stop responding.
Protocol attacks are executed at Layer 3 or 4 of the OSI model of the network like routers, firewalls, load balancers. This exploits the network by sending excessive packets to overwhelm the network and transport operations. This includes SYN floods, ping of death, DNS amplification, smurf DoS attack. The attack is measured in packets per second.
Targeting specific applications or services (e.g., HTTP floods). Application layer attack is known as Layer 7 attacks and focuses on attacking vulnerabilities of an application. Although it is a slow attack, it may directly attack the web server or CPU with an abundance of internal requests and numerous file loads resultantly cause the application to fail or crash. It includes SQL injection, HTTP flood, slowloris. The attack is measured in requests per second. However these attacks are small in numbers, it can have drastic results as CPU or web servers have low bandwidth and can be impacted with the small attacks.
Understanding what is a distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack is not enough, businesses also need to realize its implications. Some of those impacts are:
Recognizing what is a DDoS attack in action can prevent extended downtime. One of the biggest indicators of a Distributed denial of service attack is extremely slow network performance. DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) floods the network with malicious traffic to overwhelm the server crippling service for legitimate users. Page loads can take longer, responses might lag, or it could time out when trying to establish a connection.
Another set of signs of a DDoS attack is the unavailability or error of services that are typically accessible. If your site or other service suddenly becomes unreachable or developers get random error messages, this is indicative of a DDoS attack. Server performance monitoring tools can notify you when unusual spikes in traffic occur and will send alerts if there is a considerable, sudden increase in failed requests.
Spikes in traffic from a single IP address or geographic location, especially if they deviate from regular usage patterns, also suggest a possible attack. Being able to identify these red flags at an early stage enables IT teams to respond faster, which means reduced downtime and ensured service continuity.
Download the datasheet now and learn how our Active Threat Detection Solution can fortify your enterprise’s cyber environment.
DDoS attacks require a layered protection model to reduce impact and provide active network resilience. Some of the same strategies for defending against DDoS attack:
Fidelis Elevate is a complete threat detection and response platform designed to defend from all forms of cyber threats, including DDoS attacks. Fidelis Elevate provides organizations with advanced threat intelligence, endpoint monitoring and network analytics to discover and stop DDoS attacks.
In terms of DDoS protection…here is how it helps:
Real-Time Network Monitoring: Fidelis Elevate monitors network traffic in real-time, so that outliers can be identified and promptly addressed. The platform delivers red-flag alerts of abnormal spikes or any malevolent traffic flows in advance as it provides real-time visibility into traffic patterns, hence decreasing the time taken to respond.
Automated Threat Detection and Response: Fidelis Elevate effectively detects possible DDoS activities by leveraging AI-driven analytics and automation, as well can initiate automated countermeasures, like traffic filtering and rate limitation. It mitigates the DDoS attack as flooding resources before it reaches end users.
Post Attack Forensic and Investigation: After the DDoS attack, Fidelis Elevate delivers forensic capabilities to enable security teams to follow the trail of an attack. This helps you understand all attack vectors used against your organization as well as assets compromised during a successful attack. This information is crucial for strengthening the defenses and avoiding all these attacks in the future.
Fidelis Elevate provides enterprises with a DDoS attack mitigation solution and an integrated system to strengthen their overall cybersecurity posture.
A DoS attack typically originates from a single source or system, where the attacker sends an overwhelming volume of requests to the target, causing the service to slow down or crash. These attacks are relatively simpler to execute and, because they stem from one location, can often be blocked by identifying and filtering the attacker’s IP address.
On the other hand, a DDoS attack is significantly harder to execute and powerful, as it employs thousands of compromised devices (also known as “botnet”) finding floods traffic from various locations against the target. This dispersed approach makes it almost impossible to deal with DDoS attacks. Changing IPs, request types, and locations can allow them to bypass traditional security defenses which poses a major problem for network administrators who need their services available at all times while still capable of defending against such attacks.
The main purpose of a DDoS attack is to flood a specific server / network with so many requests with high traffic causing it unable to handle and eventually stopping the access for genuine users over the service/application. By exhausting system resources, attackers can create downtime, impact revenue, and damage the reputation of the targeted organization.
The basic type of DDoS attack is the Volumetric Attack, which sends a flood of data to an entire network, exhausting the bandwidth. This includes techniques such as UDP floods and ICMP floods, which overload the server and disable regular traffic.
DDoS attacks can vary in duration — lasting anywhere from a few minutes to several weeks, depending on the goal of the attacker and how much resources they have available. However, persistent attacks are often more difficult to mitigate and will last for hours and even days (which can be harmful to businesses when services need restoration).
Hey there! I'm Kriti Awasthi, your go-to guide in the world of cybersecurity. When I'm not decoding the latest cyber threats, I'm probably lost in a book or brewing a perfect cup of coffee. My goal? To make cybersecurity less intimidating and more intriguing - one page, or rather, one blog at a time!
See Fidelis in action. Learn how our fast and scalable platforms provide full visibility, deep insights, and rapid response to help security teams across the World protect, detect, respond, and neutralize advanced cyber adversaries.