Breaking Down the Real Meaning of an XDR Solution
Read More Discover effective risk-based vulnerability management strategies to safeguard your assets. Learn how
Vulnerability scanning identifies security weaknesses in IT systems, networks, and software using automated tools. This essential cybersecurity practice helps detect and fix vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them.
In this article, learn about the key features, benefits, and strategies of effective vulnerability scanning.
Vulnerability scanning is a proactive approach that focuses on identifying security weaknesses and vulnerabilities that could potentially be exploited by malicious actors. The essence of vulnerability scanning lies in its ability to automate the detection of security gaps across various IT assets, ensuring that potential threats are addressed before they can cause harm.
The significance of vulnerability scanning in cybersecurity cannot be overstated. It plays a critical role in:
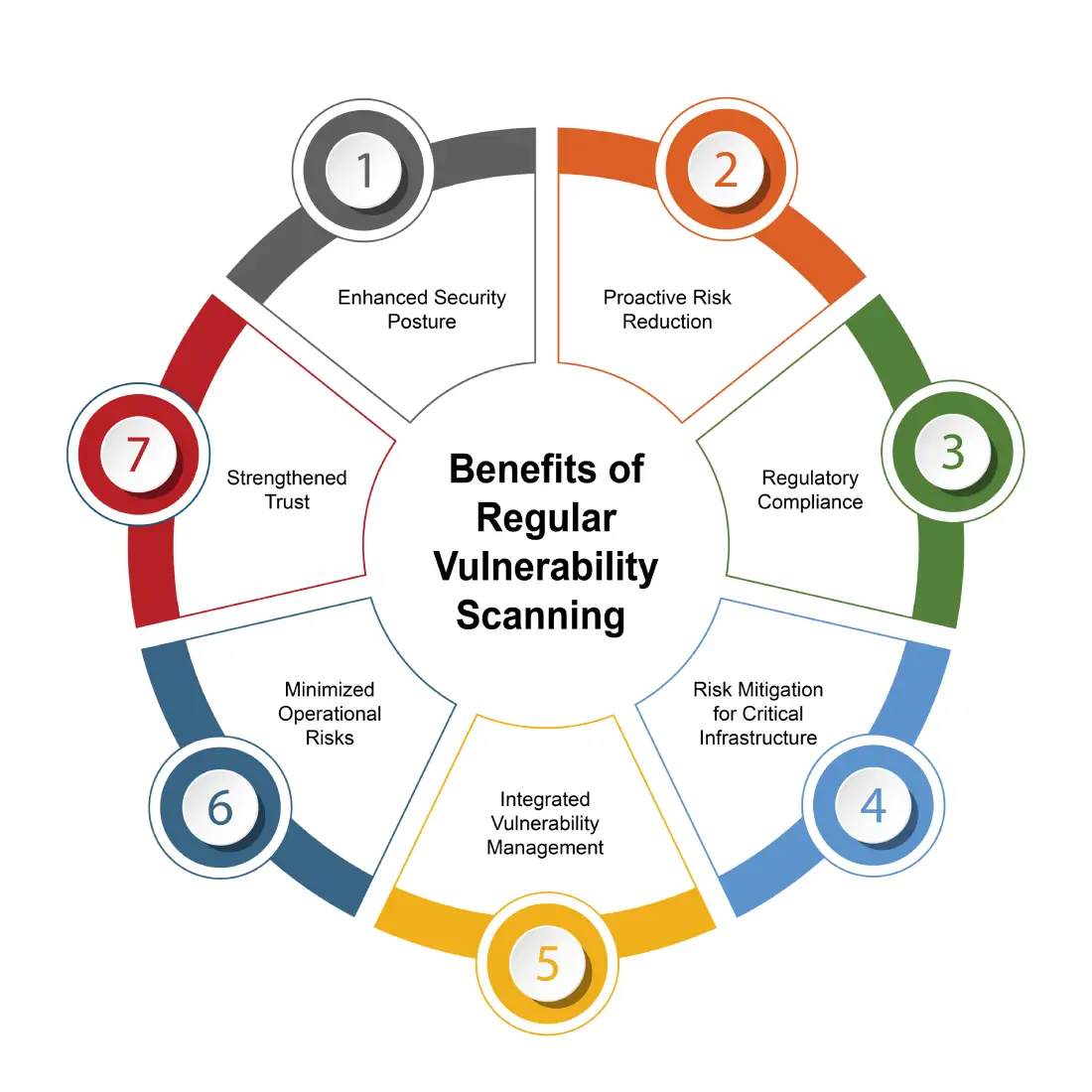
Regular scans help organizations identify and fix security weaknesses, strengthening their security posture and reducing the likelihood of successful cyberattacks. Moreover, many regulations, such as PCI-DSS, mandate regular vulnerability scanning to ensure adherence to security standards.
Regular vulnerability scanning is a cornerstone of effective vulnerability management. It enables organizations to stay ahead of emerging threats, continuously improving their security measures through web application vulnerability scanning and host vulnerability scanning. Prompt identification and addressing of vulnerabilities help businesses protect their assets and build trust with clients and stakeholders.
Ultimately, the goal is to create a resilient security framework that can withstand the evolving landscape of cyber threats.
Security vulnerabilities come in various forms, each posing unique risks to an organization.
The most common vulnerabilities are:
Understanding various types of vulnerabilities enables organizations to identify vulnerabilities and implement targeted security measures, enhancing their security posture.
The vulnerability scanning process typically includes several stages. Each of these stages plays a crucial role in ensuring a comprehensive assessment of the organization’s security posture.
Check the steps involved in vulnerability scanning:
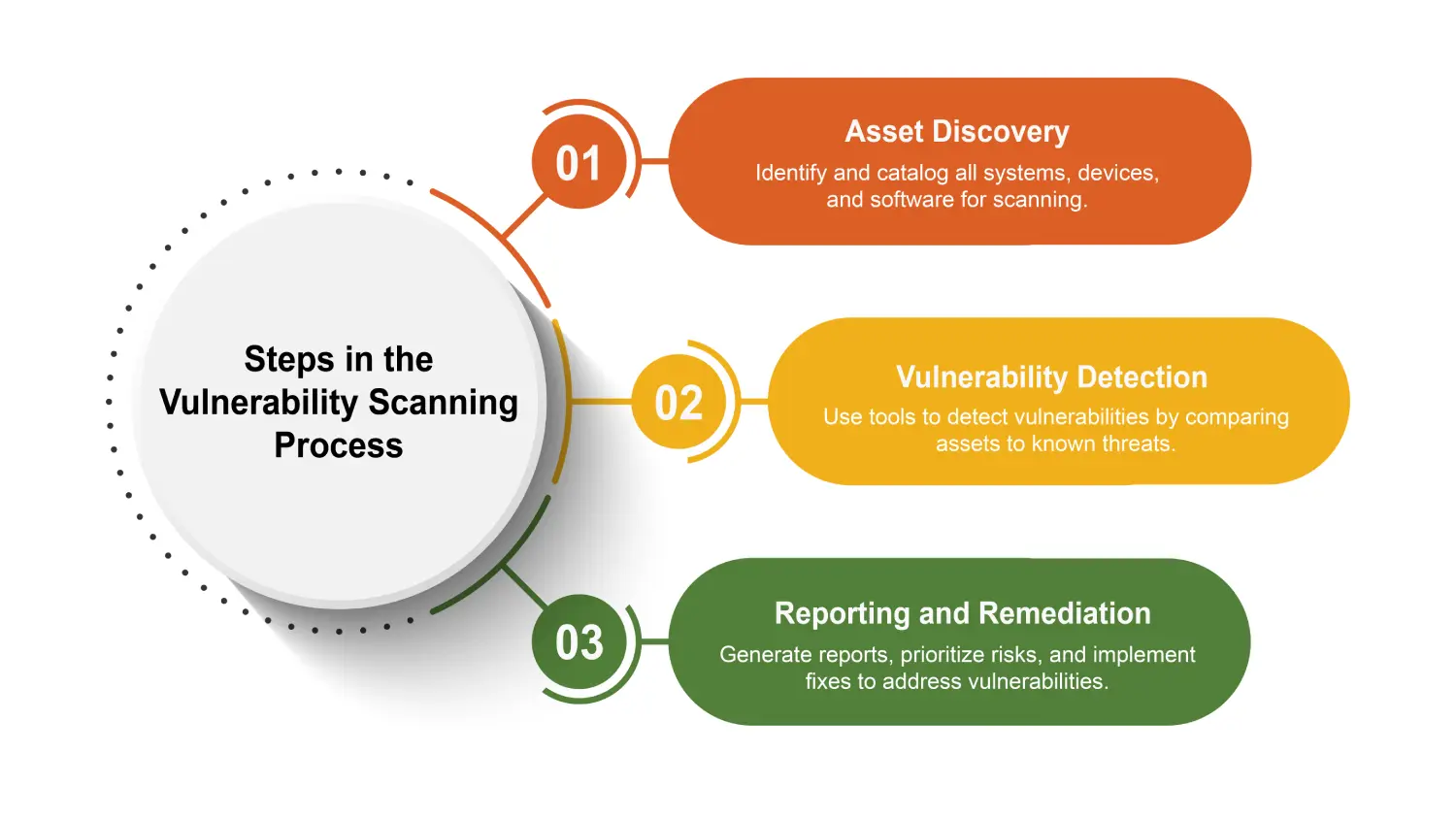
The initial step in vulnerability scanning involves asset discovery, which entails identifying and cataloging all systems, devices, and software within the organization’s network. This stage is crucial as it helps define the parameters for the scan, including target IPs or domain names, scanning intensity, and techniques. Scanners utilize various methods, such as network pings and port scans, to discover assets and ensure a thorough assessment of the network.
Additional scans may be triggered by significant network changes, such as the addition of new web servers or databases.
In this datasheet, you’ll learn:
Once assets are identified, the next step is vulnerability detection. This phase involves using automated scanning tools to compare system configurations, software versions, and network settings against known vulnerabilities databases, such as the National Vulnerability Database (NVD). These databases contain detailed information on vulnerabilities, including their severity, potential impact, and recommended mitigation techniques. The scanner assesses the system’s attack surface and can detect potential vulnerabilities based on these parameters.
The accuracy of vulnerability detection relies heavily on the quality and comprehensiveness of the vulnerability database. Effective scanners often use a combination of public sources, such as NIST and CISA, and proprietary databases to ensure a wide coverage of known security vulnerabilities. Early detection of vulnerabilities allows organizations to take proactive measures to mitigate risks and enhance security.
After detecting vulnerabilities, the next crucial step is reporting and remediation. Vulnerability scanners compile comprehensive lists of identified vulnerabilities, providing data visualization reports for review. Advanced scanners prioritize these vulnerabilities based on their criticality, often using CVSS scores or complex algorithms to assess their severity and potential business impact. This prioritization helps organizations focus their remediation efforts on the most critical flaws first.
Scanners also recommend remediation and mitigation methods for each identified vulnerability, offering actionable insights to help organizations address security weaknesses. Following remediation, it is essential to perform verification scans with a scanning tool to confirm that the vulnerabilities have been resolved.
Continuous monitoring ensures that any new vulnerabilities that may emerge are promptly detected and addressed, maintaining a strong security posture.
Vulnerability scanning can be categorized into various types, each serving a specific purpose in the overall security strategy. These include:
| Vulnerability Scan Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Internal Scanning | Internal scanning focuses on identifying vulnerabilities within an organization's internal network.
|
| External Scanning | External scanning targets vulnerabilities in internet-exposed assets, such as web servers and firewalls.
|
| Authenticated vs Unauthenticated Scans | Authenticated Scans:
|
Regular vulnerability scanning offers numerous benefits, significantly enhancing an organization’s overall security posture. These are:
Despite its benefits, vulnerability scanning comes with its own set of challenges. The challenges include:
Effective vulnerability scanners possess several key features that enhance their efficiency and accuracy. The key features are:
These features collectively enhance the effectiveness of vulnerability scanners in identifying and mitigating security risks. Tools like integrate these key features into a powerful, unified platform, offering deep visibility, automated threat detection, and seamless integration to proactively safeguard your organization’s security posture.
To optimize vulnerability scanning, organizations should implement several best practices, such as:
Scheduling regular scans is essential for adapting to evolving security risks and identifying new vulnerabilities. Organizations prioritize assets based on criticality, scanning the most crucial assets more frequently to promptly address emerging threats and strengthen overall security.
Prioritizing critical assets ensures the most vital components, like key systems and sensitive data, are secured first. This focused approach allows for efficient resource allocation, addressing vulnerabilities with the greatest potential impact.
Integrating automated vulnerability scanning tools with other security measures, such as SIEM and intrusion detection systems, enhances the overall effectiveness of the security framework. Combining these tools allows organizations to achieve a more comprehensive and coordinated defense strategy, improving threat detection and response times. Platforms like Fidelis Elevate® automate various remediation processes, allowing security teams to focus on more complex issues while improving response efficiency.
If you want to focus on comprehensive cloud vulnerability scanning, offers real-time discovery, assessment, and monitoring across hybrid-cloud environments, ensuring optimal protection and compliance for your cloud-native applications.
Vulnerability scanning is essential for identifying and addressing security weaknesses, enabling organizations to prioritize their security efforts effectively. A robust vulnerability scanning program can help organizations stay ahead of evolving cyber threats and minimize the risk of data breaches. Regularly updating and maintaining vulnerability scans is crucial to ensure that organizations can adapt to new vulnerabilities as they emerge.
Partnering with specialized services, such as Fidelis Elevate®, can enhance the effectiveness of vulnerability management by streamlining the scanning process and providing comprehensive coverage.
Vulnerability scanning is the process of automatically detecting security weaknesses in IT systems, networks, and software to prevent potential cyberattacks.
Regular vulnerability scanning helps identify and fix security flaws early, reducing the risk of cyberattacks, ensuring compliance, and improving overall security posture.
Common vulnerabilities include weak passwords, outdated or unpatched software, misconfigurations, open ports, and insecure network protocols.
Vulnerability scanning helps organizations meet regulatory standards by ensuring that security weaknesses are identified and remediated, maintaining compliance with industry-specific regulations.
Penetration testing simulates real-world cyberattacks to exploit vulnerabilities, while vulnerability scanning identifies and flags potential security weaknesses without exploiting them.
Pallavi is a tech writer with a deep enthusiasm for cybersecurity and emerging technologies. With a keen interest in digital security, she simplifies complex concepts and provides valuable insights to help businesses stay ahead and effectively navigate the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape.
See Fidelis in action. Learn how our fast and scalable platforms provide full visibility, deep insights, and rapid response to help security teams across the World protect, detect, respond, and neutralize advanced cyber adversaries.