Malware—short for malicious software and malicious programs—is one of the most dangerous cybersecurity threats today. From computer viruses and spyware to ransomware and trojans, these harmful programs are designed to:
- Sneak into systems
- Steal sensitive data
- Shut down operations entirely
Cybercriminals are constantly developing new and more advanced forms of malware. Every single day, over half a million new malware samples are discovered globally, showing just how fast these threats are evolving.
For businesses, the consequences can be severe. A single malware attack can lead to:
- Massive data loss
- Costly downtime
- Long-lasting damage to a company’s reputation
Recovering from an attack can take weeks or months and cost millions, depending on how severe and long it is.
In this blog, let’s go through the major risks malware causes and learn 5 strategies to protect your business from such malicious cyber-attacks.
Understanding Malware and Its Evolving Threat
Malware comes in many forms:
| Type of Malware | Description |
|---|---|
| Ransomware | Locks or encrypts files and demands payment to restore access. |
| Spyware | Secretly monitors user activity to steal information like passwords or payment data. |
| Virus | Attaches to files and spreads to other systems when the infected file is shared or opened. |
| Worm | Infected computers can become the breeding ground for worms, which replicate themselves and spread without needing user action. |
| Trojan (or Trojan horse) | Disguises itself as legitimate software or a computer program but contains harmful code. |
| Adware | Floods devices with pop-up ads and can introduce unwanted software or more serious threats. |
How Malware Has Changed Over Time
Malware is not only more common now, but also more advanced. In the last decade, attacks have surged, and newer types are built to get past traditional security.
Modern malware is much harder to detect and stop. For example:
- Polymorphic malware changes its code to avoid detection.
- Fileless malware hides in system memory, leaving no trace on hard drives.
- Social engineering tricks people into clicking links, downloading files, or giving access.
- Obfuscation methods disguise malicious code to look harmless, confusing both users and antivirus tools.
How Malware Gets In
Attackers don’t rely on just one method—they exploit multiple weak points to increase their chances of success. Here are the most common entryways:
| Source of Threat | Description |
|---|---|
| Phishing Emails | Look real but contain links or attachments that lead to malicious websites. |
| Compromised Websites | Automatically download harmful software without your knowledge (drive-by downloads). |
| Removable Media | USB drives left in public or shared between devices can spread malware. |
| Unverified Software | Computer software from unofficial sources or peer-to-peer networks may carry malware. |
| Outdated Software | Contains security flaws that hackers can easily exploit, particularly on personal computers if they are not regularly updated. |
- Behavior analysis and machine learning
- Real-time & offline scanning capabilities
- In-depth detection rates and case study data

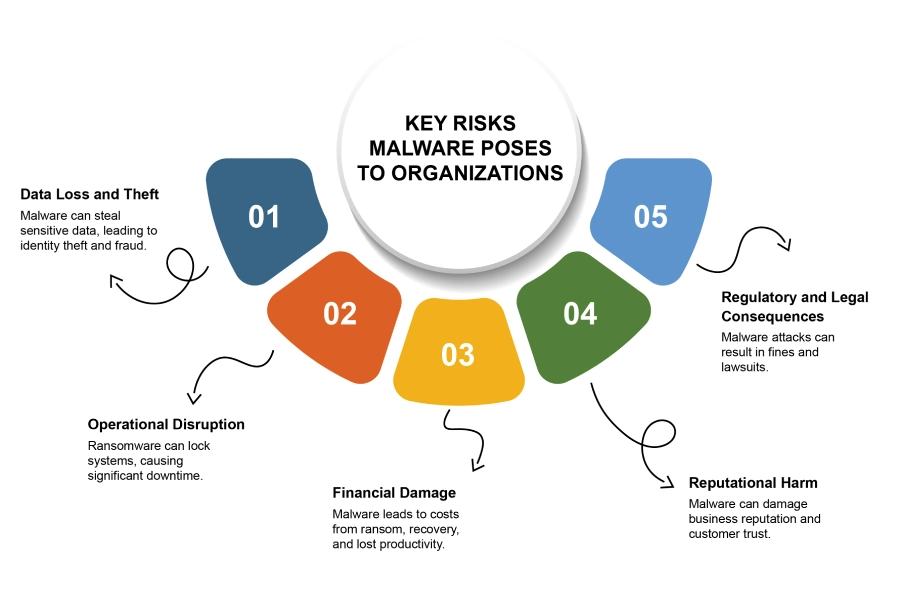
Key Risks Malware Poses to Organizations
-
Data Loss and Theft
Malware, including mobile malware, can pose a serious risk to sensitive information.
It can steal or compromise:- Personal details
- Financial data
- Intellectual property
- Customer records
- Identity theft
- Financial fraud
- Industrial espionage
-
Operational Disruption
Malware can seriously disrupt business operations by providing remote access to cybercriminals. Ransomware, a kind of malware, can:
- Lock infected systems
- Encrypt important files, making them inaccessible
- Demand a ransom payment for file recovery
- Delayed recovery
- Significant downtime
- Major disruption to services
-
Financial Damage
Malware attacks can have a significant financial impact. Costs may include:
- Ransom payments (if applicable)
- System recovery and data restoration expenses
- Efforts to mitigate further damage
- Lost productivity
- Operational downtime
- Customer dissatisfaction
-
Reputational Harm
A single malware attack can seriously hurt a company's reputation. If sensitive data gets leaked and operations get destroyed, it can lead to the loss of trust and loyalty from:
- Customers
- Business partners
- Regulators
- Decline in customer loyalty
- Harder to get new customers
- More attention from regulators
-
Regulatory and Legal Consequences
Organizations must follow data protection laws. A malware attack can lead to serious legal trouble, such as:
- Non-compliance fines
- Lawsuits
Businesses may be held liable for failing to protect customer data. This can further harm the organization’s reputation and financial stability.
These risks highlight why protecting against malware is essential for any organization. In the next section, we’ll discuss effective strategies to safeguard your business from these threats.
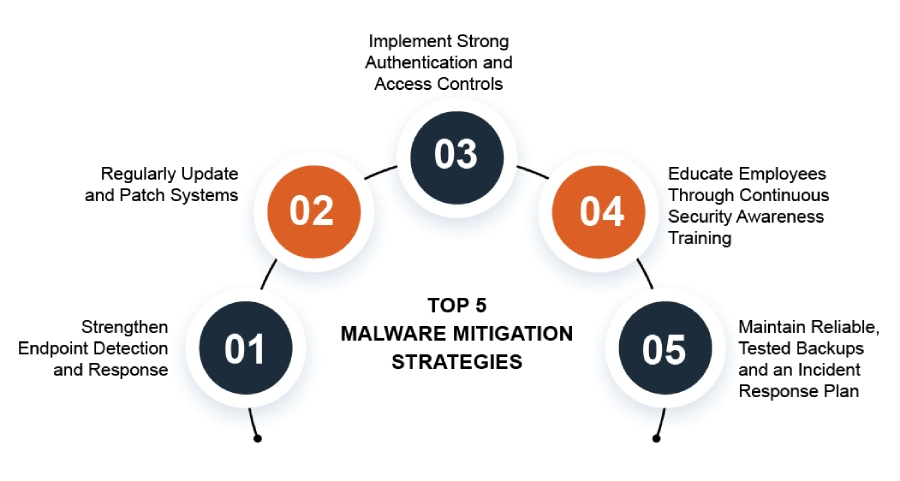
Top 5 Malware Mitigation Strategies
Follow these strategies to manage and reduce malware attacks in your organization:
-
Strengthen Endpoint Detection and Response
Endpoint security solutions (EDR) are key for detecting and responding to malware in real time.
EDR tools utilize advanced technologies like:- Behavioral analysis
- Machine learning
Key capabilities include:- Detecting unusual activity across the network
- Reanalyzing previously approved files and flagging malicious ones
- Quickly isolating threats to prevent further spread
-
Regularly Update and Patch Systems
Regular updates are a key defense against malware. Old software often has weaknesses that hackers target.
Key areas to keep updated include:- Operating systems
- Browsers
- Plugins
Regular patching helps address known vulnerabilities promptly. Automating patch management helps in:- Reducing the risk of human error
- Ensuring critical updates are not missed
-
Implement Strong Authentication and Access Controls
Enforcing strong authentication practices is crucial to preventing unauthorized access.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Use MFA on all critical systems and accounts for added security beyond passwords.
- Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP): Give users access only to what they need to lower security risks.
- Conditional Access Policies: Require things like MFA or location limits before allowing access to sensitive systems.
-
Educate Employees Through Continuous Security Awareness Training
Malware often spreads due to human mistakes like phishing attacks and downloading malicious files.
Continuous security awareness training helps employees:- Stay informed about the latest threats
- Recognize and avoid suspicious activity
Effective training strategies include:- Simulated phishing tests
- Providing real-world threat examples
- Promoting a culture of quick, blame-free reporting
-
Maintain Reliable, Tested Backups and an Incident Response Plan
Attacks can still occur despite strong preventive measures. Reliable and regularly tested backups are essential for data recovery.
The backup strategy should include:- Offline backups
- Cloud backups
An Incident Response Plan (IRP) should guide the team through:- Detection – Quickly identifying the attack to mitigate its impact
- Containment – Isolating the threat to prevent further spread
- Recovery – Restoring affected systems and data to normal operation
Speed is critical during incident response because:- Regulatory bodies may require rapid data recovery to meet legal and industry standards.
- It reduces business disruption and limits damage from the attack.
These strategies help businesses stay safer from malware and limit damage from attacks.
Bonus Best Practices for a Stronger Defense
To further bolster your defenses against malware, consider these additional best practices:
-
Monitor Network Traffic for Unusual Activity:
Continuous network monitoring helps identify suspicious behavior early.
It involves:- Tracking traffic patterns
- Flagging anomalies
-
Segment Networks to Contain Malware:
Network segmentation helps contain malware infections.
It involves separating different parts of your network to:- Limit the spread of malware
- Reduce the risk of widespread attacks
-
Review Physical and Digital Security Regularly:
Cybersecurity involves both digital and physical security. Regularly assess both to ensure comprehensive protection.
Key areas to review include:- Access controls
- Device security
- Digital security protocols
By using these best practices along with key security strategies and a strong cybersecurity tool, your organization can create a more effective defense against attacks.
Fidelis Elevate®: A Powerful Malware Detection Solution
Fidelis Elevate® offers a comprehensive, multi-layered approach to malware detection and response, combining:
- Network security
- Endpoint protection
- Active Directory protection
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
- Deception technologies
It uses advanced sandboxing, machine learning, and behavioral analysis to detect and analyze suspicious files and URLs in real time.
- Understand malware behavior
- Identify malware evasion behaviors
- Share malware forensics

Key features of Fidelis Elevate® include:
-
-
Real-Time Threat Analysis:
Suspicious files are instantly sent to the sandbox for detailed checks, helping detect and respond quickly.
-
Customizable and Automated:
Users can create custom rules, automate responses, and integrate with other security tools to stay ahead of evolving threats.
-
Continuous Threat Intelligence:
Fidelis combines internal and external threat data to keep defenses up to date.
Overall, Fidelis gives organizations smart, automated protection and fast threat response!
Conclusion
Malware threats need to be handled immediately and cautiously, as a single threat is enough to stop entire business operations and lose company reputation. By implementing the key strategies we discussed above and adopting a robust XDR tool like Fidelis, businesses can cope with malware attacks and improve their cyber hygiene!
Frequently Ask Questions
What is malware?
Malware is malicious software designed to harm or exploit a computer system. It includes:
- Viruses
- Spyware
- Ransomware attacks, and more.
How does malware affect businesses?
Malware can steal sensitive data, disrupt operations, cause financial losses, and damage a company’s reputation.
What are the top strategies to protect against malware?
The key strategies include:
- Strengthening Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
- Regularly updating systems
- Implementing strong authentication
- Training employees on security
- Maintaining backups and an incident response plan.



