Cyber risk involves possible losses from cyber-attacks and data breaches. For businesses, these risks can lead to financial loss, reputational damage, and operational disruptions. This article will help you understand cyber risk, its impacts, and strategies for effective management.
What is Cyber Risk?
Cyber risk refers to the potential for loss or exposure resulting from an attack or data breach impacting an organization. At its core, cyber risks encompass the various threats that can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, and operational disruptions. Imagine an organization suddenly losing access to its critical data or having sensitive customer information exposed; the fallout can be devastating.
The consequences of cyber risk are far-reaching. In an age where consumer data is a prized asset, maintaining its security is paramount. Moreover, business disruption caused by cyber-attacks can bring activities to a standstill, affecting productivity and service delivery. The increasing threat of cyber-attacks and data leaks highlights the need for organizations to adopt robust risk management practices. Continuous vigilance and proactive measures can significantly mitigate risks and safeguard critical assets.
Consequences of Cyber Attacks
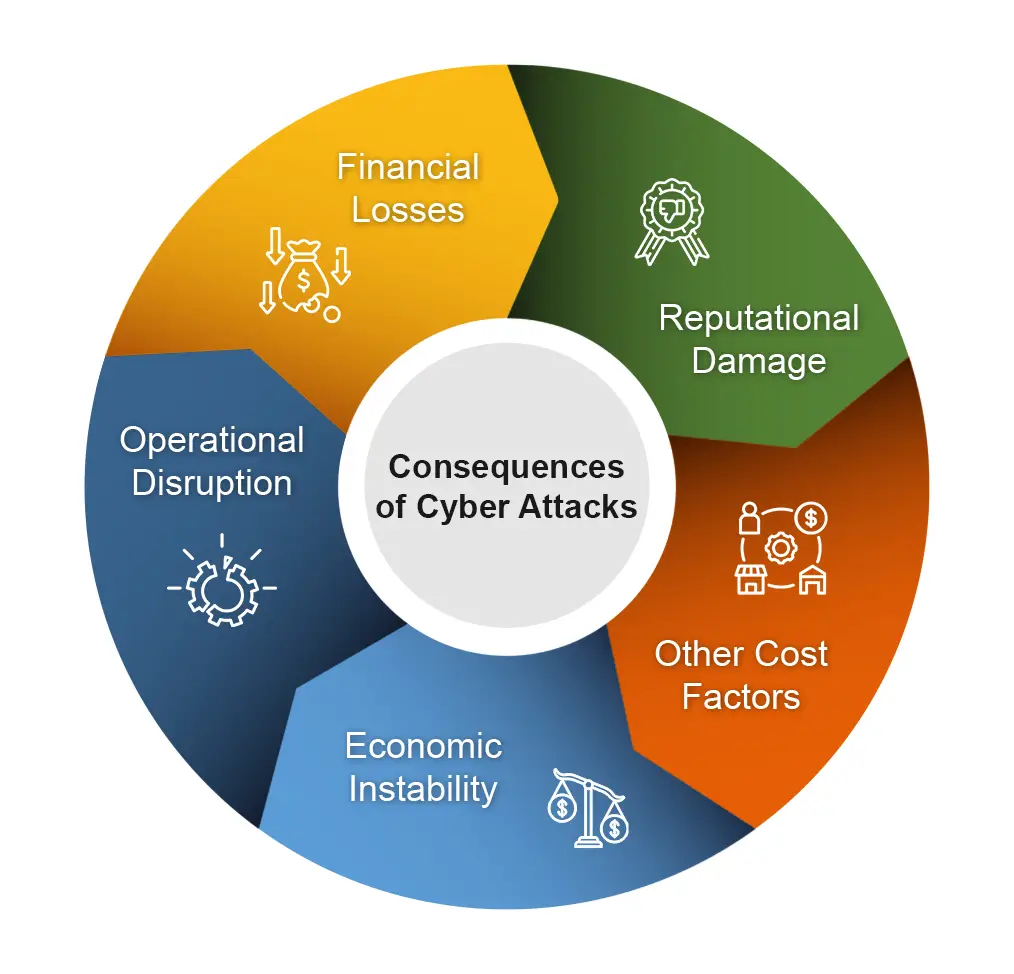
Cyber attacks can have profound implications for businesses, often resulting in substantial setbacks.
- Financial losses: According to reports, cyber incidents have caused losses exceeding $2.5 billion, a fourfold increase since 2017.
- Other Cost factors: Expenses include business disruption, reduced revenue, legal fees, and regulatory fines.
- Reputational damage: Loss of customer trust and brand reputation can impact current and future business.
- Economic Instability: In case of financial institutions, attacks can undermine public confidence, disrupt services, and threaten economic stability.
- Business disruption: Ransomware attacks can cause widespread service outages, affecting multiple organizations.
Common Cyber Risks
Organizations face a myriad of cybersecurity risks, with third-party and fourth-party vendors adding to the complexity. These vendors can be a weak link if they do not maintain strong security practices, potentially leading to data breaches and disruptions. Maintaining continuous visibility and monitoring vendor activities are crucial for managing these risks.
Insider threats also pose significant cybersecurity risks. Employees with authorized access can misuse their privileges, either intentionally or unintentionally, compromising sensitive information. A Zero Trust Security model, which limits access based on job function, can help mitigate these threats. This approach ensures that no one has more access than necessary, reducing the risk of exploitation.
Protecting sensitive customer data is paramount. Robust encryption and access controls are essential to prevent unauthorized access. Comprehensive policies to assess and manage vendor risks, along with regular assessments and continuous monitoring, form the backbone of a strong cybersecurity posture.
Threat Actors in Cybersecurity
Threat actors in cybersecurity can be broadly categorized into three main groups:

Cyber criminals
They generally seek financial gain, engaging in activities like data theft or ransom. Often driven by straightforward financial motives, they pose a persistent threat to businesses.

Malicious insiders
These are individuals within an organization who exploit their access to harm the organization, often for personal gain or revenge.

Nation-state actors
These are government-sponsored groups that engage in cyber espionage or cyber warfare, targeting other nations or organizations for strategic advantages.
Malicious insiders, misuse their authorized access to compromise an organization’s information. These individuals are often driven by personal motives such as revenge or financial gain. Insider knowledge makes them particularly dangerous, capable of exploiting vulnerabilities that external attackers might miss.
Nation-state actors engage in cyber activities on behalf of governments, often driven by political or economic motives. These actors are typically involved in espionage or pursuing political objectives, utilizing advanced techniques to infiltrate networks for sensitive information. The number of tracked threat actors has surged from 300 to over 1,500 in just one year.
Evolving Cyber Threats
The nature of cyber threats is constantly evolving, with cyber actors and nation-states enhancing their capabilities to disrupt, destroy, or threaten essential technologies devices and media services firms defence organizations. Organizations need to stay ahead of these threats by constantly updating and improving their security teams’ infrastructure.
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) plays a crucial role in this effort by sharing up-to-date information about high-impact security activities and analyzing new threats. This information helps organizations better understand and prepare for evolving threats.
In this rapidly changing landscape, a comprehensive risk management approach is essential. By enhancing visibility into an organization’s cybersecurity status and readiness, such an approach allows for proactive measures to combat threats. Fidelis, for example, enhances threat detection abilities across various stages of the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
Assessing Cyber Risk
A thorough cyber risk assessment is the foundation of effective risk management. This process involves systematically identifying vulnerabilities and threats within an organization’s IT infrastructure. Conducting a data audit is essential for establishing a comprehensive inventory of IT assets and prioritizing security measures.
Identifying both internal and external threats is crucial for a thorough cyber risk assessment. Risk levels are evaluated by analyzing the likelihood and potential impact of a cyberattack on critical assets. Reputable frameworks, such as MITRE ATT&CK, can aid in identifying threats relevant to each asset.
To mitigate risk specific risks identified during the assessment, organizations should implement targeted security controls. Monitoring and documenting the results of the assessment help ensure continuous improvement in security posture. This iterative process is vital for adapting to ever-evolving risks.
Effective Cyber Risk Management Strategies
Effective cyber risk management strategies are essential for safeguarding organizational assets. A multi-layered defence strategy includes:
- Robust firewalls
- Regular software updates
- Employee training
- Proactive monitoring
- Encryption technologies
- Strict access controls
These measures work together to create a resilient security posture.
Zero Trust principles enhance security effectively. By limiting access based on job function, Zero Trust ensures that no one has more access than necessary. Using AI for comprehensive threat detection can significantly boost an organization’s defensive capabilities. AI technologies are viewed as essential for mitigating cyber threats and addressing the talent shortage in the cybersecurity field.
Proactive network monitoring allows for early detection of unusual patterns or potential breaches. Automation can significantly enhance efficiency in risk management processes, enabling faster and more accurate threat detection. Regular testing of the overall security posture helps evaluate defenses against threats.
Post-incident evaluations are essential for enhancing defenses against future cybersecurity threats. Learning from past incidents enables organizations to strengthen security measures and reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
The Role of Incident Response
Incident response is a critical component of cybersecurity, as it mitigates the impact of cyberattacks and ensures a quick and effective response. An incident response plan should outline immediate actions post-breach, communication protocols, and recovery steps. Testing and updating the incident response plan regularly ensures its relevance and effectiveness against new threats.
A well-defined incident response plan helps organizations minimize the damage caused by cyber-attacks and recover more swiftly. This proactive approach is essential for maintaining business continuity and protecting sensitive information.
Fidelis Elevate Powers Incident Response Success
- Detecting attackers real-time
- Streamlined security stack for network, endpoint and deception
- Building automated response playbooks
Employee Training in Cybersecurity
Employee training in cybersecurity is vital for enhancing defensive capabilities. Educating staff on phishing, secure passwords, and company policies enables them to recognize and mitigate risks. Regular training keeps employees updated on the latest threats and best practices in cybersecurity.
Insider threats can arise from employees who misuse their access to sensitive information. Interactive and engaging training methods increase the effectiveness of employee training in cybersecurity. Fostering a culture of security awareness can significantly reduce the risk of cyber attacks.
Compliance Requirements vs. Actual Security
Security measures focus on protecting organizational assets, while compliance involves adhering to established standards from external entities. Organizations may implement security measures that do not fully align with compliance standards, leading to potential vulnerabilities. Compliance failures can result in significant penalties, highlighting the importance of third-party vendors adhering to industry regulations.
Achieving compliance means following guidelines set by standards organizations, but security requires continuous evaluation and adaptation beyond those guidelines. While compliance can enhance security, it does not ensure that all security gaps are addressed within the organization. Ongoing monitoring of regulatory changes ensures internal controls remain compliant with external requirements.
How Fidelis Network® Enhances Cybersecurity
Fidelis Network® provides comprehensive visibility across all network ports and protocols, enabling detailed monitoring for potential threats and malicious activities. Coupling deep visibility with risk assessment, Fidelis Network® profiles, classifies, and identifies risky assets and users. This level of visibility is crucial for proactive threat hunting and detection.
Automated risk-aware terrain mapping visualizes network traffic and identifies risky assets, boosting threat detection capabilities. Network behavior anomaly detection, deep session inspection, and data loss prevention technology protect against data exfiltration and other security events. These capabilities allow Fidelis Network® to respond to network threats significantly faster than traditional methods, achieving detection of post-breach attacks over nine times quicker.
Fidelis Network® also integrates automated threat hunting to enhance incident response and operational resilience. Deception technology enables early identification of attackers, improving threat intelligence. Rich, indexable metadata aids in rapid threat detection and effective investigations.
In summary, Fidelis Network® offers a robust and comprehensive solution for enhancing cybersecurity, helping organizations stay ahead of evolving cyber threats.
Final Thoughts on Cyber Risk Management
Effective cyber risk management is vital for safeguarding organizational resources and maintaining customer trust. By identifying and mitigating cybersecurity threats, the organisation’s risk management function needs can protect their assets and maintain a positive relationship with customers.
Proactive and effective cyber risk management is essential for protecting assets and maintaining customer trust. Organizations must remain vigilant and adaptive, continuously evolving their strategies to address the ever-changing landscape of cyber threats and participate in cyber risk roundtables.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the essence of cyber risk and its implications for businesses in 2025. From understanding common cybersecurity risks to assessing threats and implementing effective risk management strategies, we’ve covered the critical aspects of safeguarding organizational assets.
Effective cyber risk management is not just about compliance but involves continuous evaluation, adaptation, and proactive measures. By staying ahead of evolving threats and leveraging advanced technologies like Fidelis Network®, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity posture and build lasting trust with their customers.
Frequently Ask Questions
What is the NIST definition of cyber risk?
NIST defines cyber risk as the risk associated with relying on cyber resources, including systems or elements that operate in or intermittently access cyberspace. This definition emphasizes the inherent dependencies in digital environments.
What are the business implications of cyber attacks?
Cyber attacks can result in significant financial losses, harm to your company’s reputation, and disruption of operations, ultimately affecting your bottom line and long-term viability. It’s crucial to prioritize cybersecurity measures to mitigate these risks effectively.
How can organizations manage third-party vendor risks?
Organizations can effectively manage third-party vendor risks through continuous visibility, regular assessments, and the implementation of robust security policies. Taking these steps ensures a proactive approach to risk management.
What is the role of incident response in cybersecurity?
Incident response is crucial in cybersecurity as it helps to quickly mitigate the impact of cyberattacks, minimizing damage and facilitating recovery processes. A well-executed incident response plan is essential for maintaining organizational resilience against threats.
How does Fidelis Network® enhance cybersecurity?
Fidelis Network® enhances cybersecurity by offering comprehensive visibility and automated threat detection, enabling rapid response to threats and significantly improving an organization’s overall security posture.



