Breaking Down the Real Meaning of an XDR Solution
Read More Discover essential strategies to enhance your security posture with XDR for achieving
Want to stay ahead of threats in 2025? This research report is all you need to stay updated.
What is Zero Trust Architecture? It is a security model that continuously verifies every user and device accessing network resources. Unlike traditional models, it never implicitly trusts entities inside or outside the network. Zero Trust is crucial for defending against modern cyber threats and securing today’s IT environments.
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is a security framework designed to protect modern IT environments that are increasingly porous and distributed. Traditional security models often rely on perimeter-based defenses, implicitly trusting entities within the network.
Zero Trust eliminates implicit trust by strictly verifying every access request, so no entity, internal or external, accesses without thorough validation. This approach is crucial in today’s landscape, where cyber threats can originate from anywhere, and breaches are inevitable. Implementing zero trust models enhances security measures significantly within a zero trust network, aligning with the zero trust security model and supporting zero trust implementation as part of a zero trust strategy in a zero trust enterprise. Additionally, zero trust network access is essential for maintaining robust security.
Zero Trust integrates users, applications, and infrastructure into a comprehensive security framework, leveraging automation to enforce protocols and respond to risks effectively. The result is a robust security posture that adapts to the dynamic nature of modern IT environments, supported by a trust strategy.
At the heart of Zero Trust Architecture are several key components that work together to create a secure environment. The first is identity verification, which ensures that both human and non-human users are correctly identified before access is granted. This process includes validating the user identity of users and devices. It utilizes methods such as multi-factor authentication, embedded chips, and behavior analytics. All devices must comply with Zero Trust principles, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring they meet necessary security standards.
Another critical component is micro segmentation, a technique that limits how users and applications can move within the network. By dividing the network into smaller segments, organizations can apply granular access controls, restricting access based on specific roles and tasks. This reduces the potential attack surface and minimizes the impact of a breach, especially when compared to traditional network segmentation.
Together, these components form the core pillars of Zero Trust Architecture: identity verification, device compliance, and micro segmentation.
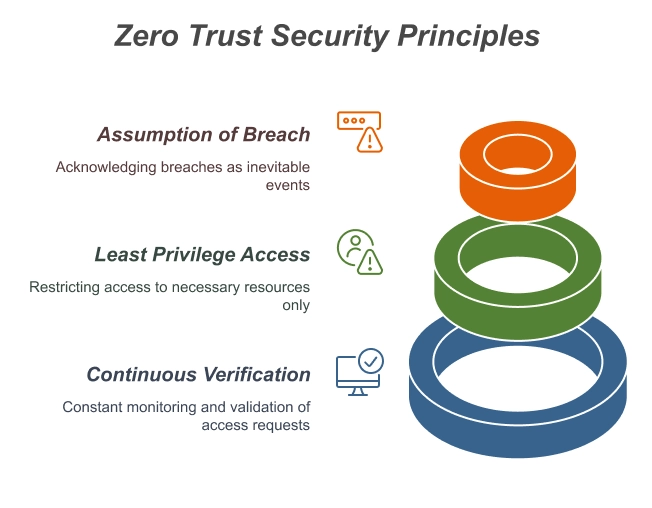
Zero Trust Architecture is based on three core principles. These are continuous verification, least privilege access, and the assumption of breach. These principles collectively ensure that security is maintained at all times, with no entity trusted by default.
Continuous verification involves constantly monitoring and validating access requests, while least privilege access restricts users’ access rights to only what is necessary for their roles. The assumption of breach principle operates under the premise that breaches can and will happen, both from inside and outside the organization.
Adopting these principles significantly enhances an organization’s cybersecurity posture, reducing potential attack surfaces and mitigating threats.
In the Zero Trust model, trust is not a one-time event but a continuous process. Continuous verification ensures that users and devices are constantly monitored and authenticated before being granted access. This is achieved through automated threat detection mechanisms that integrate with monitoring processes to identify security issues promptly.
Continuous validation of user and device behaviors allows Zero Trust Architecture to quickly detect and respond to anomalies, safeguarding cloud environments and ensuring only authenticated users access sensitive resources.
Least privilege access is a cornerstone of Zero Trust principles, meaning that users and devices only access what they absolutely need. Access is tailored to specific tasks and granted only when necessary, enforcing least privilege access. This dynamic approach ensures that access policies adapt to changing user behaviors and environmental conditions.
Automation plays a key role in this process, allowing access policies to change in real-time based on contextual factors such as device type and location. Enforcing granular access controls minimizes security risks and enhances overall security posture.
The assumption of breach principle acknowledges that breaches are inevitable. Zero Trust Architecture aims to minimize the blast radius of a breach by micro-segmenting resources, implementing end-to-end encryption, and continuously monitoring behavior. This approach enhances incident response by providing granular control, allowing organizations to quickly identify and isolate compromised resources while adopting an assume breach mindset.
Assuming that breaches can occur, Zero Trust Architecture significantly reduces their impact, protecting critical assets and maintaining network integrity.
Adopting Zero Trust Architecture offers numerous benefits, particularly in enhancing security, reducing risks, and improving compliance. In today’s complex and distributed IT environments, Zero Trust provides a robust framework that minimizes the attack surface and ensures continuous verification of all access requests. This approach is increasingly adopted across various sectors to mitigate risks associated with data breaches and cyber threats.
Implementing a Zero Trust model fosters a culture of security awareness within organizations, leading to long-term cost savings by lowering the costs associated with data breach mitigation. Additionally, the technical framework and structure of Zero Trust Architecture provide improved compliance with regulatory standards, simplifying audit processes and demonstrating a commitment to data protection within a trust security model.
Zero Trust Architecture greatly improves security by reducing the attack surface. It achieves this through the use of multifactor authentication and the enforcement of strict access controls. Continuous monitoring and logging provide enhanced visibility over network activities, allowing security teams to detect and respond to threats more effectively.
Fidelis Elevate®, a leading platform in Zero Trust strategies, incorporates AI-driven analysis and deception technologies to improve threat detection capabilities, ensuring continuous risk assessment and dynamic threat monitoring.
Adopting Zero Trust frameworks ensures continuous authentication of users and devices, regardless of location, enhancing cloud security and protecting sensitive data.
Zero Trust Architecture enforces strict access controls, ensuring that users only have access to the resources they need, significantly reducing the risk of data breaches and potential insider threats. Following the principle of least privilege minimizes exposure or damage from compromised accounts.
These stringent access management practices are crucial in reducing the likelihood of insider threats, as access is limited to essential functions only. Overall, Zero Trust Architecture provides a robust security framework that effectively minimizes risks and enhances the organization’s security posture.
Zero Trust Architecture assists organizations in meeting regulatory standards like GDPR and HIPAA by enforcing strong access controls and multifactor authentication. Zero Trust frameworks help organizations align with various regulatory standards by demonstrating a commitment to data protection.
Enforcing security policies to keep sensitive data secure and monitored, Zero Trust architectures facilitate regulatory compliance, simplifying audits with clear access logs and compliance reports. Continuous monitoring and maintaining detailed audit trails are essential practices that enhance compliance management and ensure regulatory requirements are met.
Discover how Fidelis Elevate® powers real-time visibility, automated response, and intelligent deception to elevate your security posture. What you’ll gain from this resource:
Implementing Zero Trust Architecture requires adopting new technologies, processes, and mindsets to redefine security enforcement. A structured approach is essential to effectively implement Zero Trust, ensuring that all aspects of the security framework are addressed.
This section provides a step-by-step guide to implementing Zero Trust Architecture, covering the identification of critical assets, verification of users and devices, definition of access policies, and continuous monitoring and maintenance. By following these steps, organizations can establish a robust Zero Trust framework that enhances their overall security posture and mitigates potential threats.
Identifying critical assets is a crucial first step in implementing Zero Trust Architecture. Understanding which data points and assets are most critical allows organizations to prioritize protection efforts and minimize vulnerabilities.
Automation within Zero Trust architecture assists in the enforcement of security protocols and in responding to threats promptly. Focusing on critical assets allows organizations to strengthen their overall security posture and ensure that their most valuable resources are adequately protected.
Verifying users and devices is essential to ensure secure access within a Zero Trust framework. Implementing strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication and device health checks, is vital to verify user identities and device compliance, as well as to support various security functions.
Authentication policies should consider various factors, including users’ and workflows’ characteristics, device, location, origin, time of access, and recent activity. Device compliance checks are essential before granting access to ensure they meet security requirements, preventing unauthorized users from gaining access to sensitive data.
Defining access policies is crucial in managing who can access what resources within a Zero Trust Architecture framework. The principle of least privilege access ensures that users are only granted access to the resources necessary for their roles. Granular access controls, just-in-time (JIT), and just-enough access (JEA) are methods used to enforce least privilege within Zero Trust.
Automating access policies based on user roles and workflows enhances security and efficiency within the organization, ensuring that access is granted dynamically based on real-time assessments.
Continuous monitoring of network traffic is critical to identifying abnormal activities and ensuring security within a Zero Trust Architecture. Regular updates of systems are crucial to maintain the effectiveness of Zero Trust Architecture, ensuring that security measures remain up-to-date.
Ongoing risk evaluation is required to adapt access policies in real-time, based on the changing threat landscape and threat intelligence. Organizations must be prepared for breaches and implement effective security strategy response strategies to minimize the impact.
Before deploying Zero Trust architectures, it is essential to test them for threat effectiveness and user productivity impact.
Fidelis Elevate® is a leading Extended Detection and Response (XDR) platform designed to enhance security through advanced threat detection and response capabilities. Integrating closely with Zero Trust principles, Fidelis Elevate® provides comprehensive monitoring, continuous authentication, and adaptive response to threats.
This section will explore how Fidelis Elevate® supports Zero Trust strategies, emphasizing its role in reinforcing a security-aware environment and ensuring strict access controls as part of the federal zero trust strategy.
Fidelis Elevate® aligns with Zero Trust principles by enabling organizations to proactively identify and respond to potential threats before they escalate. The platform enforces strict access controls based on user roles, ensuring that only authorized users gain access to sensitive resources.
It provides comprehensive monitoring and real-time activity tracking across various environments, maintaining the strict access controls inherent in Zero Trust frameworks. Integrating advanced analytics and automated response capabilities, Fidelis Elevate® supports a robust Zero Trust security posture, reinforcing overall organizational security infrastructure.
Zero Trust Architecture has proven effective across various real-world scenarios, demonstrating its versatility and robustness. In remote work environments, Zero Trust secures sensitive data by enforcing strict access controls and continuous verification, ensuring that employees can work remotely without compromising security.
For cloud security, Zero Trust manages multi-cloud access through consistent access policies and continuous monitoring, protecting sensitive data and maintaining compliance. Additionally, Zero Trust enhances IoT device management by ensuring each device is authenticated and continuously monitored, addressing the unique security challenges posed by the proliferation of IoT devices.
These applications highlight the practical benefits and adaptability of Zero Trust Architecture in securing modern IT environments.
The adoption of Zero Trust helps organizations secure remote workers by enforcing strict identity verification and access controls. This model emphasizes continuous verification, making zero trust adoption well-suited for remote access work where security perimeters are often undefined. To enhance security further, organizations should implement a zero trust framework and learn more about zero trust.
By requiring multifactor authentication and continuously monitoring user activities, Zero Trust ensures that sensitive data remains secure while enabling employees to work from anywhere without compromising the integrity of the corporate network. This approach effectively addresses the security challenges associated with remote work environments, providing a robust framework for protecting critical assets.
Zero Trust Architecture is essential for securing cloud environments, as it eliminates implicit trust and mandates continuous verification of all access requests. By verifying user identities and device compliance continuously, Zero Trust ensures secure access to cloud resources, protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Access policies are defined based on user roles and workflows, effectively managing multi-cloud access control and maintaining consistent security processes and security measures across different cloud platforms. A cloud access security broker can enhance these efforts.
Real-world applications of Zero Trust in cloud environments demonstrate its effectiveness in safeguarding data and ensuring regulatory compliance, particularly for remote workforces and IoT device management.
The proliferation of IoT devices introduces numerous security challenges, including vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers. Zero Trust Architecture enhances security for IoT devices by enforcing strict access controls and continuous authentication. Implementing a Zero Trust model significantly reduces the risk of data breaches associated with IoT devices.
Validating the identities and compliance of all devices is crucial in a Zero Trust framework, especially for IoT devices that may lack built-in security. Defining access policies based on roles and maintaining continuous monitoring are essential practices to secure IoT devices, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive data.
In summary, Zero Trust Architecture represents a paradigm shift in cybersecurity, eliminating implicit trust and enforcing continuous verification of all access requests. By adhering to core principles such as continuous verification, least privilege access, and the assumption of breach, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture and mitigate risks associated with cyber threats. The adoption of Zero Trust not only improves security but also reduces risks and ensures compliance with regulatory standards. Platforms like Fidelis Elevate® play a critical role in supporting Zero Trust strategies, providing advanced threat detection and response capabilities that reinforce a security-aware environment. As cyber threats continue to evolve, embracing Zero Trust Architecture is essential for protecting critical assets and maintaining the integrity of modern IT environments.
Zero Trust enhances security by minimizing the attack surface and enforcing strict access controls, alongside requiring multifactor authentication and continuously monitoring network activities. This comprehensive approach significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and potential breaches.
Fidelis Elevate® bolsters Zero Trust strategies through comprehensive monitoring, continuous authentication, advanced threat detection, and automated response capabilities, fostering a security-aware environment.
Sarika, a cybersecurity enthusiast, contributes insightful articles to Fidelis Security, guiding readers through the complexities of digital security with clarity and passion. Beyond her writing, she actively engages in the cybersecurity community, staying informed about emerging trends and technologies to empower individuals and organizations in safeguarding their digital assets.
See Fidelis in action. Learn how our fast and scalable platforms provide full visibility, deep insights, and rapid response to help security teams across the World protect, detect, respond, and neutralize advanced cyber adversaries.